Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a significant concern in both medical and emergency settings, necessitating prompt and accurate diagnosis. Among the many neurological indicators, the pupillary response stands out as a crucial metric. By measuring the pupils’ reactions, healthcare professionals can gain critical insights into the severity and location of a brain injury. This article explores how pupillary response, particularly through the use of modern neurological tools and precise pupil measurement techniques, indicates brain trauma.
The Role of Pupillary Response in Traumatic Brain Injury
The pupillary response in traumatic brain injury (TBI) refers to the way pupils react to light and other stimuli following a head injury. In a healthy individual, the pupils constrict (become smaller) when exposed to bright light and dilate (become larger) in low-light conditions. This reaction, known as the pupillary light reflex, is controlled by the autonomic nervous system and is a vital part of a comprehensive neuro exam.
In the context of TBI, abnormal pupillary responses can indicate increased intracranial pressure, brainstem herniation, or other severe neurological issues. Abnormalities might include unequal pupil sizes (anisocoria), sluggish or non-reactive pupils, or pupils that do not constrict properly.
The Importance of Pupil Measurement
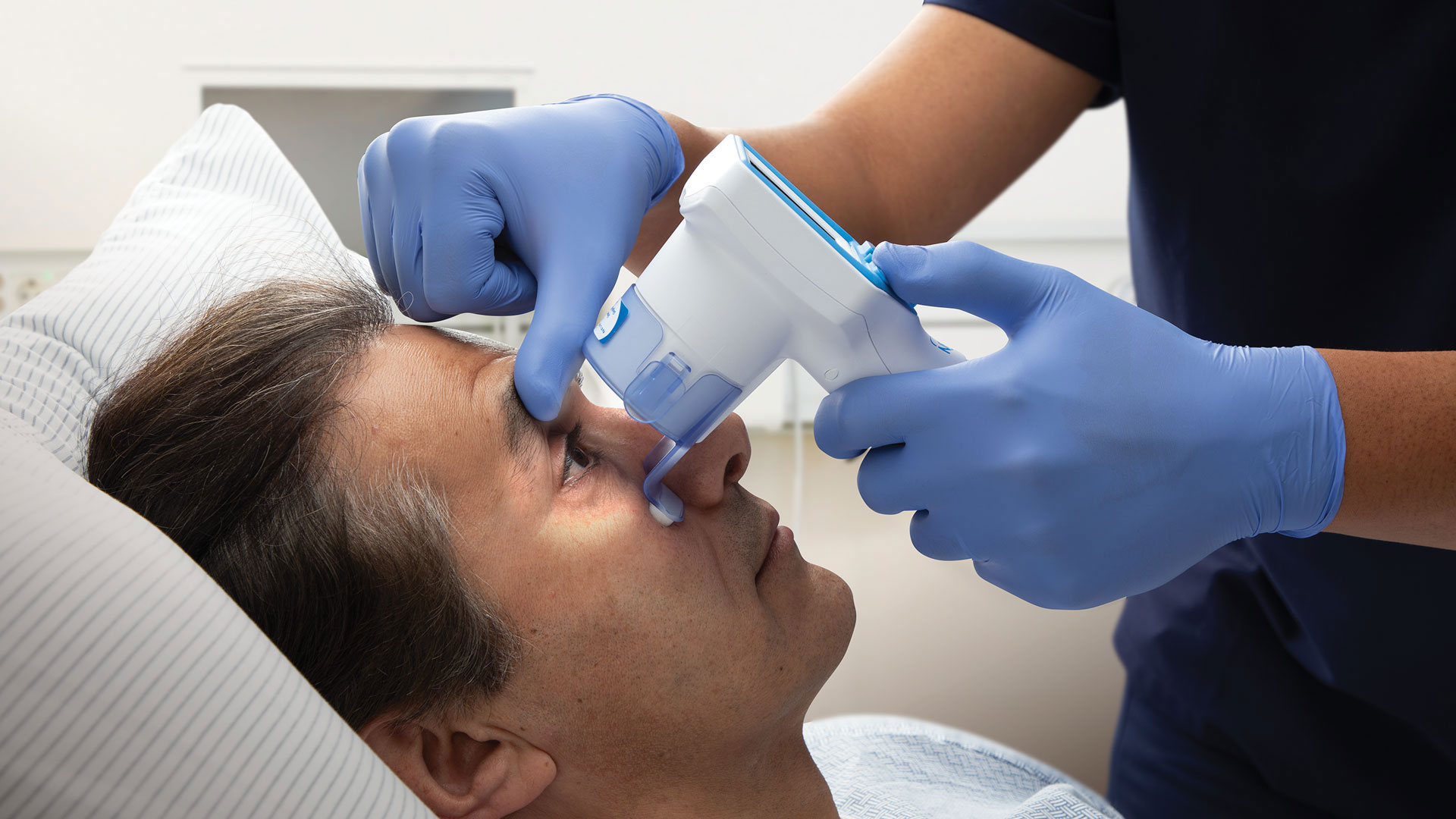
Accurate pupil measurement is essential in assessing the pupillary response in patients with suspected brain trauma. Traditional methods of measuring pupil size and reactivity involved subjective assessment by medical personnel using a flashlight. However, this method can be prone to human error and inconsistency.
Modern neurological tools like the NeuroOptics NPi-200 Pupillometer have revolutionized the way pupil measurements are taken. These devices provide precise, quantitative data on pupil size, reactivity, and symmetry. The NeuroOptics NPi, for instance, uses infrared light to measure the pupil’s response to a standardized light stimulus, offering an objective and reproducible assessment. This tool helps eliminate the variability associated with manual measurements and ensures that even subtle changes in pupillary response are detected.
Pupillary Light Reflex: A Critical Component of Neuro Exams
The pupillary light reflex is an integral part of a comprehensive neuro exam, which assesses various neurological functions to identify potential brain injuries. During this reflex, light is shone into each eye separately, and the response of both the illuminated and the non-illuminated pupil is observed.
In patients with TBI, deviations from normal pupillary light reflex can provide critical clues. For example, a blown pupil (one that remains large and unresponsive to light) may indicate severe brain trauma and the need for immediate intervention. Similarly, asymmetrical responses can point to localized brain injuries or pressure on specific cranial nerves.
Neurological Tools Enhancing Pupillary Assessments
Advancements in neurological tools have significantly improved the accuracy and reliability of pupillary assessments. The introduction of automated pupillometers, like the NeuroOptics NPi, has allowed for precise measurements that are critical in emergency and intensive care settings. These devices measure the Neurological Pupil Index (NPi), a scale that quantifies pupil reactivity. An NPi score below the normal range can be an early warning sign of neurological deterioration.
The use of such tools is particularly beneficial in situations where rapid decision-making is crucial. For instance, in emergency rooms and trauma centers, the ability to quickly and accurately assess pupillary response can guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
Integrating Pupillary Response in Trauma Protocols
Integrating pupillary response assessments into trauma protocols is essential for ensuring comprehensive patient evaluations. Emergency medical personnel, paramedics, and neurosurgeons should be trained in using automated pupillometers and interpreting their results. This integration helps in creating standardized protocols that can be consistently applied across various medical settings.
Moreover, continuous monitoring of pupillary response in patients with severe head injuries can provide ongoing insights into their neurological status. Changes in pupil size or reactivity over time can indicate improvement or deterioration, helping guide treatment adjustments and interventions.
Conclusion
The pupillary response is a vital indicator of brain trauma, providing essential insights into the severity and location of injuries. Accurate pupil measurement using advanced neurological tools like the NeuroOptics NPi-200 Pupillometer enhances the reliability of these assessments. By integrating pupillary response evaluations into trauma protocols, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions, improve patient outcomes, and provide timely interventions in cases of traumatic brain injury. As technology continues to advance, the role of pupillary assessments in neurological examinations will only become more significant, ensuring better care for patients with brain injuries.
Keep an eye for more news & updates on Web of Buzz!